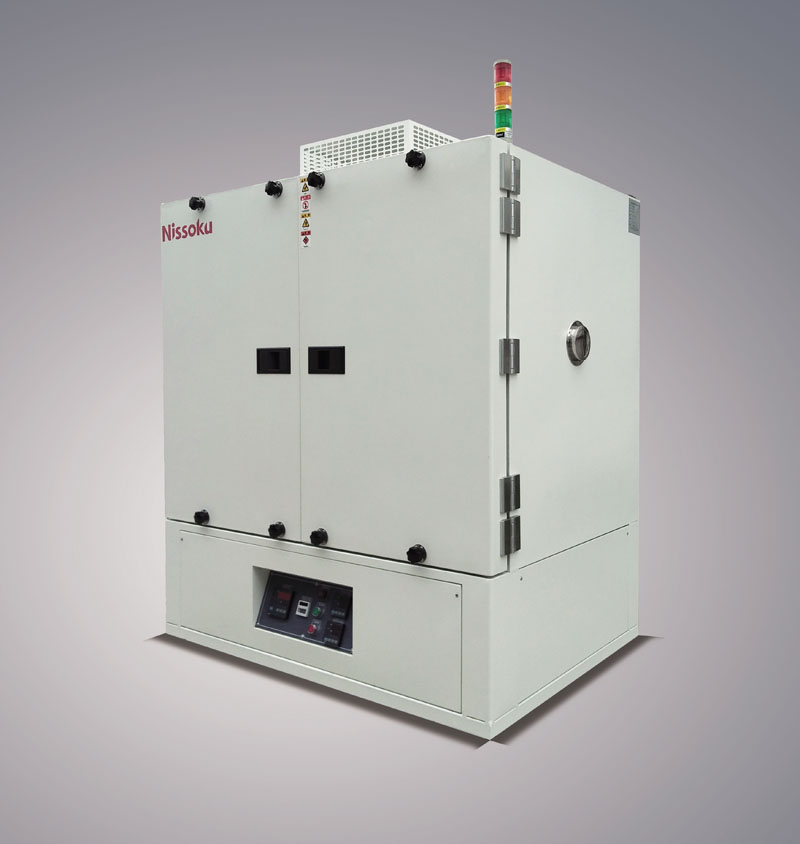
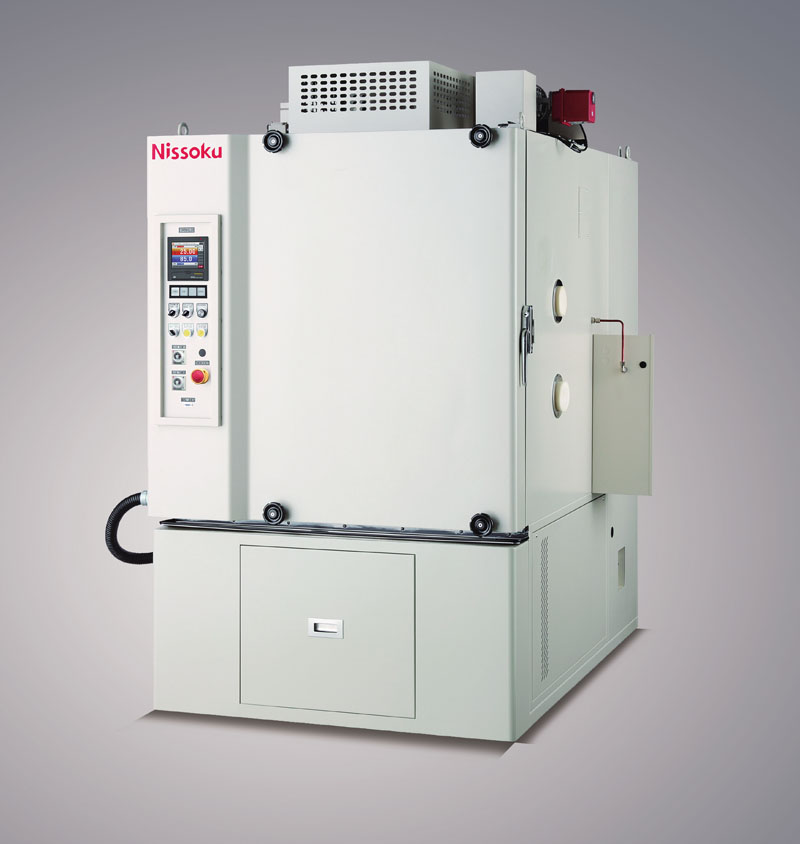
Power batteries generate heat during operation, especially in high rate charging and discharging or high-temperature environments. Temperature related tests in environmental reliability testing, such as high-temperature storage and high-temperature cycling tests, can simulate these extreme situations. Through testing, it can be determined at what temperature the battery will show signs of thermal runaway. For example, in high-temperature cycling tests, the battery repeatedly switches between high temperature (such as 60 ℃) and room temperature. If the battery's heat dissipation system or the thermal stability of the battery material is poor, it may cause the internal temperature of the battery to rise sharply, leading to thermal runaway. Thermal runaway is a very dangerous situation that may cause battery fires or explosions. Therefore, environmental reliability testing is crucial for preventing thermal runaway and ensuring the safety of battery use.

- GB/T 31467.3
- GB/T 31485
- GB 38031
- IEC 62660-3
- ISO 12405-3
- UN 38.3
- UL 2580