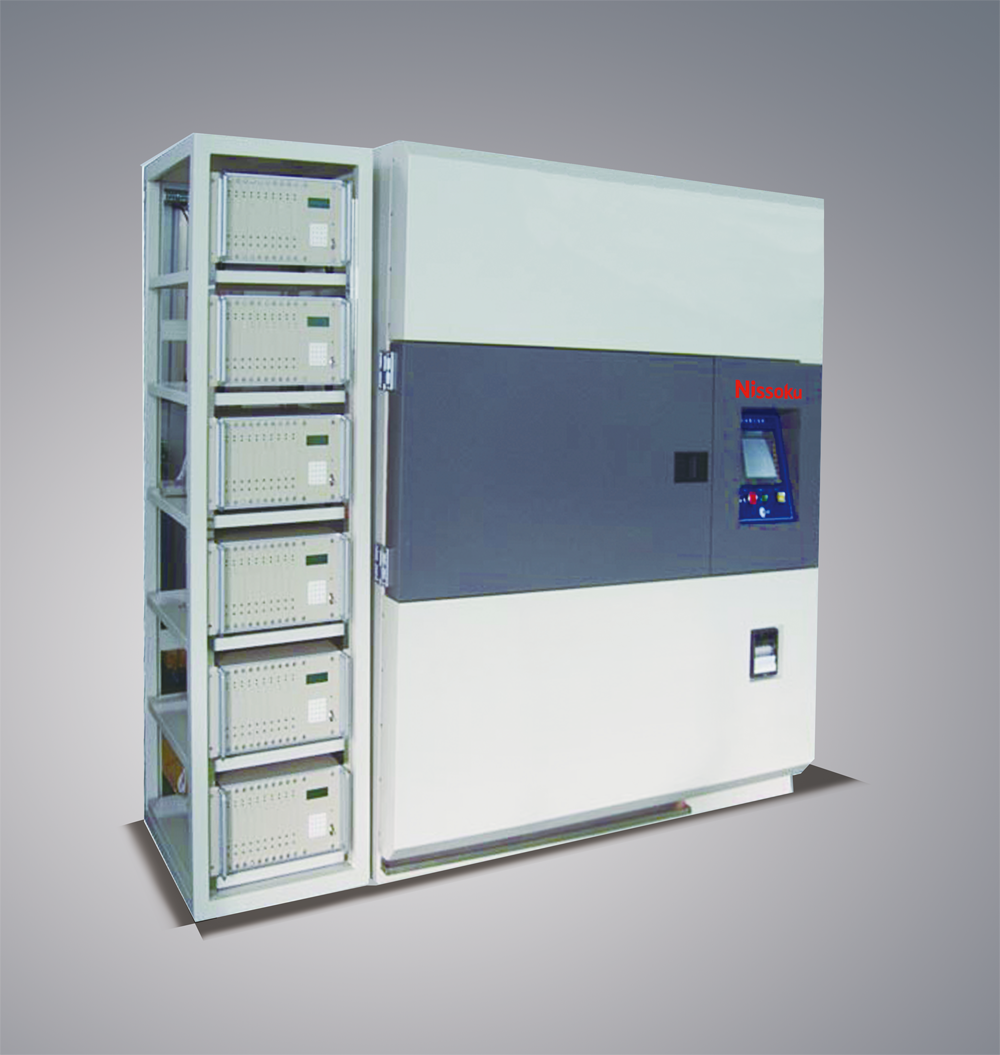
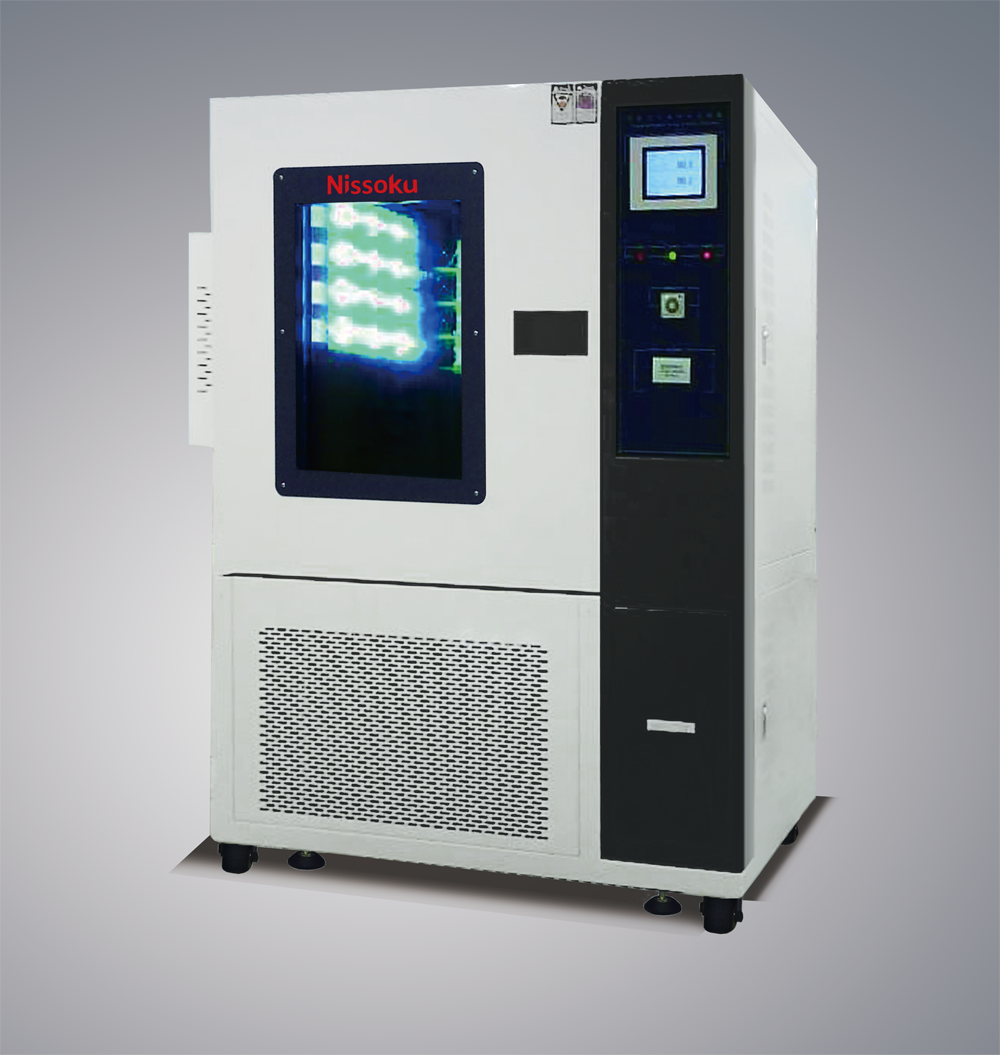
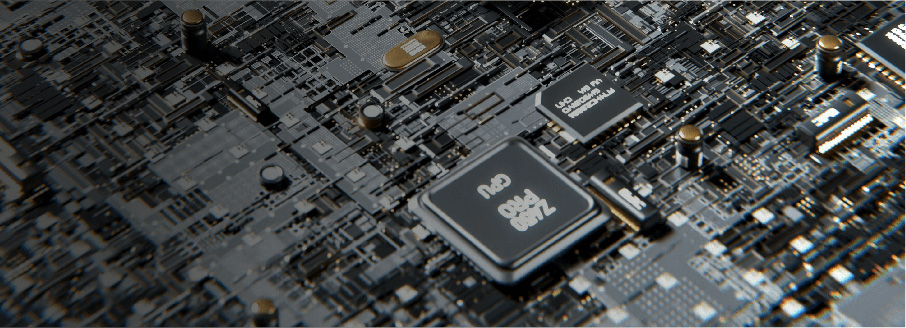
The performance of PCB includes electrical performance (such as insulation resistance, dielectric constant, etc.) and signal transmission performance (such as signal integrity, transmission delay, etc.). The wet heat test in environmental reliability testing (such as in an environment with a temperature of 40 ℃ and a relative humidity of 90%) can evaluate the insulation performance of PCBs in high humidity environments. High humidity may cause moisture on the surface of the PCB, leading to a decrease in insulation resistance and causing electrical faults such as short circuits. In addition, in terms of signal transmission, temperature changes can affect the resistivity of copper foil on PCB. Temperature cycling tests (from -40 ℃ to 85 ℃) can observe the changes in signal transmission performance of PCB at different temperatures, ensuring that the performance of PCB can meet design requirements under various environmental conditions.
- GB/T 2423
- GB/T 4677
- IPC-TM-650
- IEC 60068
- IPC-9701
- JEDC JESD22
- MIL-STD-810
- MIL-STD-202